Troubleshooting
If something is not working as expected, start here. This page groups the most common VBA Padlock issues by area, with practical fixes you can apply immediately.
Quick Diagnosis Flow
Section titled “Quick Diagnosis Flow”- Compile first with F5 and fix every error in the Messages panel.
- Validate scripts in Test Runner before testing from Office.
- Re-inject VBA Bridge after any Security Code / project changes.
- Check
bin/deployment (all expected DLLs present, not blocked). - If licensing is involved, verify activation settings and key/project match.
Compilation Issues
Section titled “Compilation Issues”Compilation fails with errors
Section titled “Compilation fails with errors”Cause: The VBA Padlock script contains syntax errors, unsupported functions, or references to undefined variables.
Solution:
- Check the Messages panel for specific error messages and line numbers.
- Review VBA Compatibility for unsupported features (e.g., no class modules, no
Declarestatements, no Office object model access inside scripts). - Ensure all functions used are either user-defined or from the built-in script libraries.
Compilation succeeds but functions return errors at runtime
Section titled “Compilation succeeds but functions return errors at runtime”Cause: The compiled function exists but encounters a runtime issue (wrong parameter count, type mismatch, etc.).
Solution:
- Test your function in the Test Runner before injecting into Office.
- Verify you are passing the correct number and types of parameters to match the compiled function’s signature.
- Check the return value —
VBAPL_Executereturns aVariantthat may contain an error code.
VBA Bridge Injection Issues
Section titled “VBA Bridge Injection Issues”Injection fails or fails to create the VBA Bridge in Office
Section titled “Injection fails or fails to create the VBA Bridge in Office”Cause: VBA Padlock requires programmatic access to the Office VBA project to automate the injection of the bridge module. This access is disabled by default in Office for security reasons.
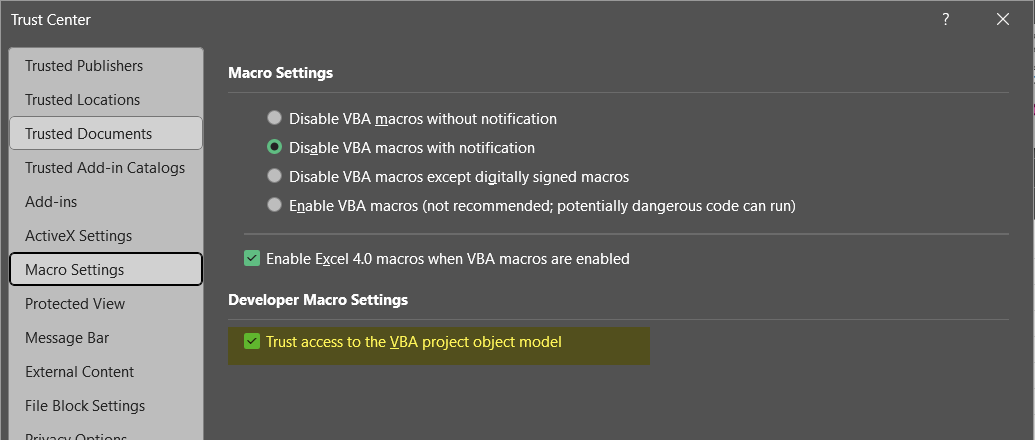
Solution: You must enable “Trust access to the VBA project object model” in your Office application settings:
- Open the Office application (Excel, Word, etc.).
- Go to File > Options.
- Select Trust Center in the left menu.
- Click the Trust Center Settings… button.
- Select Macro Settings in the left menu.
- Under Developer Macro Settings, check the Trust access to the VBA project object model box.
- Click OK and restart the Office application.
DLL Loading Issues
Section titled “DLL Loading Issues””DLL not found” or “File not found” error
Section titled “”DLL not found” or “File not found” error”Cause: The Office file cannot find the DLL files.
Solution:
- All three DLLs must be in a
bin/subdirectory relative to the Office file:MyWorkbook.xlsmbin\├── MyWorkbookrun32.dll├── MyWorkbookrun64.dll└── MyWorkbook.dll - Verify the
bin/directory exists and contains all three DLLs. - If the files were downloaded from the internet, right-click each DLL → Properties → check Unblock.
“Verification failed” or Security Code mismatch
Section titled ““Verification failed” or Security Code mismatch”Cause: The Security Code in the VBA Bridge does not match the one in the satellite DLL. This happens when you recompile without re-injecting the VBA Bridge.
Solution:
- In VBA Padlock, click Create VBA Bridge → Inject Into Office.
- Recompile with F5.
- Use Publish Final DLL to build the final version.
DLL signature verification failed
Section titled “DLL signature verification failed”Cause: A DLL file was modified after compilation, or a file is corrupted.
Solution:
- Recompile the project from VBA Padlock.
- Do not modify or patch the DLL files after compilation — they are integrity-verified.
- If the issue persists, try deleting the
bin/directory and rebuilding.
Licensing Issues
Section titled “Licensing Issues”
Trial period not starting
Section titled “Trial period not starting”Cause: License storage permissions or conflicting installations.
Solution:
- Ensure the user has write access to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER(registry storage) or to the application folder (.LICfile storage). - Check the storage mode in Activation Settings.
- If using portable mode, verify the
.LICfile can be created next to the Office file.
License key rejected
Section titled “License key rejected”Cause: The key format does not match, the key was generated for a different project, or the Hardware ID does not match.
Solution:
- Verify the key was generated with the same project (matching Security Code and ECC keys).
- Check for typos — common confusions:
0vsO,1vsl,Ivsl. - If using hardware-locked keys, verify the user’s System ID matches the one used to generate the key.
- Use the Key Generator to regenerate the key if needed.
Hardware ID changed unexpectedly
Section titled “Hardware ID changed unexpectedly”Cause: A hardware component used for the Hardware ID was replaced or updated (new hard drive, network adapter, etc.).
Solution:
- Check which components are selected in Hardware ID Options.
- Remove volatile components (e.g., MAC address) if users frequently change hardware.
- Generate a new key for the user’s updated Hardware ID. See Key Generation guide.
Online activation/deactivation fails
Section titled “Online activation/deactivation fails”Cause: Network issues, incorrect server URL, or server configuration problems.
Solution:
- Verify the activation URL in Online Activation Settings.
- Test the server connection from VBA Padlock using the Test Connection button.
- Ensure the server uses HTTPS and the PHP activation kit is correctly deployed. See Activation Server guide.
- Check the server error logs for details.
Runtime Issues
Section titled “Runtime Issues”Functions work in Test Runner but fail in Office
Section titled “Functions work in Test Runner but fail in Office”Cause: The Office file may have an outdated Bridge module, or macros may be disabled.
Solution:
- Re-inject the VBA Bridge: Create VBA Bridge → Inject Into Office.
- Verify macros are enabled in Office Trust Center settings.
Anti-virus false positive
Section titled “Anti-virus false positive”Cause: Some antivirus software flags DLLs with certain protection patterns as suspicious.
Solution:
- This is a false positive. VBA Padlock runtime DLLs are digitally signed by G.D.G. Software.
- Submit the DLL to your antivirus vendor for whitelisting.
- Add the
bin/directory to your antivirus exclusion list.
Office Compatibility
Section titled “Office Compatibility”32-bit vs 64-bit Office
Section titled “32-bit vs 64-bit Office”VBA Padlock generates both 32-bit and 64-bit runtime DLLs. The VBA Bridge automatically detects the Office architecture and loads the correct DLL. No configuration is needed.
Office version compatibility
Section titled “Office version compatibility”Compiled DLLs are compatible with Office 2016 and later, including Microsoft 365 desktop apps. The VBA Bridge uses Declare PtrSafe syntax for 64-bit compatibility.
Multiple Office files sharing the same DLL
Section titled “Multiple Office files sharing the same DLL”Each Office file needs its own satellite DLL (compiled with its own Security Code). The runtime DLLs ({DLLName}run32.dll and {DLLName}run64.dll) are also project-specific, named after the project’s DLL name.
Support for Windows ARM
Section titled “Support for Windows ARM”Issue: Office ARM is installed, and VBA Padlock DLLs fail to load.
Cause: Native ARM versions of Office cannot load standard x86 or x64 DLLs.
Solution:
- On Windows ARM (like Surface Pro 11, Surface Laptop 7, or Snapdragon X Elite devices), uninstall the ARM-native version of Office and install Office 64-bit instead.
- Office 64-bit on Windows ARM uses Microsoft’s Prism emulation. This allows the standard x64 versions of VBA Padlock DLLs to load and execute seamlessly without any modifications.
Getting Help
Section titled “Getting Help”If your issue is not covered here:
- Check the License Return Codes for error code meanings
- Review the VBA Compatibility page for supported features
- Visit the FAQ for additional answers
- Contact support for personalized assistance