Protect Excel
Similar workflow tailored for Excel workbooks. Read the guide →
You have built a Word document with VBA macros — maybe it generates contracts from templates, fills in client details automatically, or produces formatted reports — and you need to distribute it without exposing your source code.
In this tutorial, you’ll walk through the complete workflow: compiling your VBA logic into a protected DLL, wiring it up to Word through the auto-generated VBA Bridge, and optionally adding activation keys with hardware locking.
Time needed: 15-20 minutes
Imagine you sell a “Document Builder” tool: users open a Word template containing placeholders like {CUSTOMER_NAME}, click a button, and the macro fills everything in, adds a formatted table, and exports the result to PDF.
VBA Padlock allows you to commercialize this tool while keeping your proprietary logic completely hidden inside a native DLL.
Start by opening your Word file in VBA Padlock to create a project that will hold your compiled code and licensing settings.
Launch VBA Padlock from the Start menu.
Click “Open Office File” in the ribbon and select your .docm or .dotm file (for example, DocumentBuilder.docm).
Set Project Information
In the Project Info tab:
Document Builder).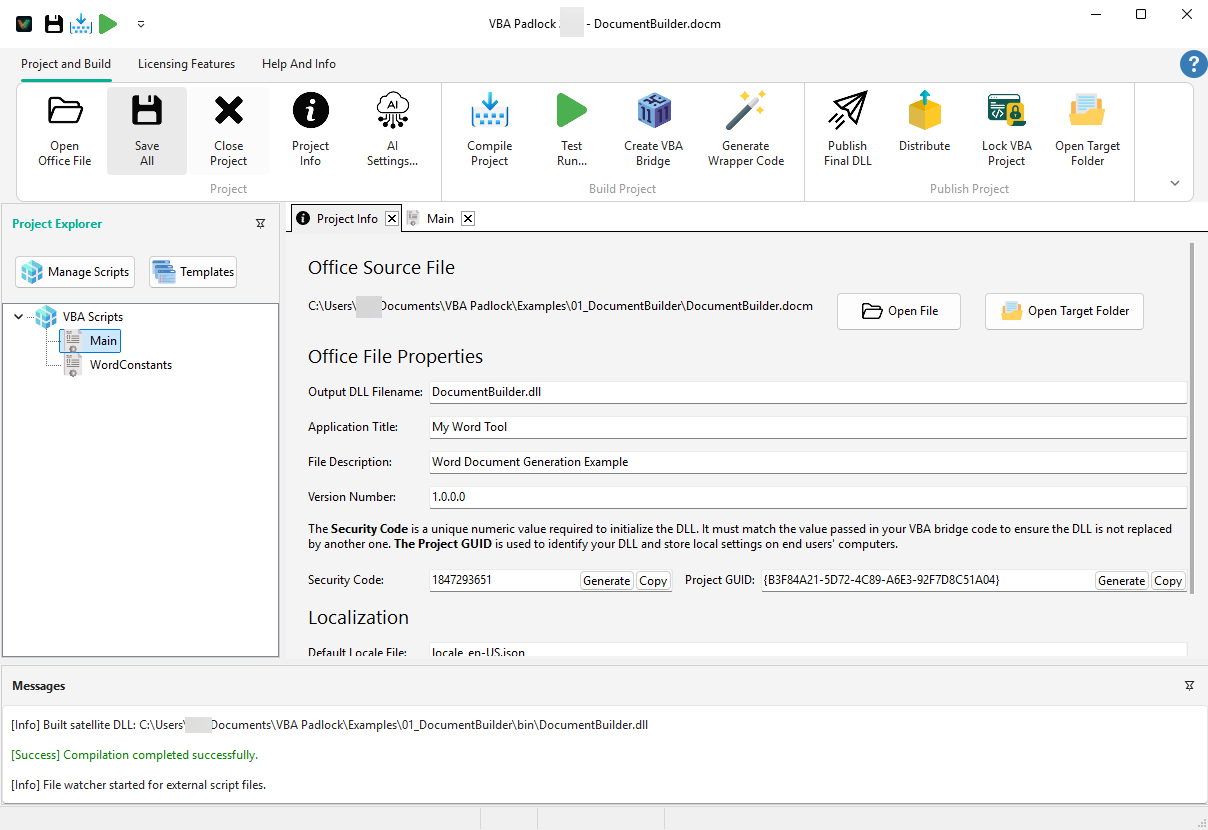
Switch to the Code Editor. This is where you write the VBA logic you want to hide. Below is an excerpt based on the real DocumentBuilder example included with VBA Padlock.
' Main.bas -- Compiled into the DLL' These functions access Word's object model via the "Application" object.
Sub HelloWorld() MsgBox "Hello from VBA Padlock!" & Chr(13) & Chr(13) & _ "Document Builder is ready.", _ vbInformation, "VBA Padlock - Word"End Sub
'-------------------------------------------------------------------------------' Get current document information' Returns: Formatted string with document stats'-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Function GetDocumentInfo() Dim Doc Dim Info
Set Doc = Application.ActiveDocument
Info = "Document: " & Doc.Name & Chr(13) Info = Info & "Pages: " & Doc.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticPages) & Chr(13) Info = Info & "Words: " & Doc.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticWords) & Chr(13) Info = Info & "Characters: " & Doc.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticCharacters)
GetDocumentInfo = InfoEnd Function
' Replace placeholders like {CUSTOMER_NAME} with actual dataFunction ReplacePlaceholders(Placeholders) Dim Doc, i, Parts, Key, Value, Count Set Doc = Application.ActiveDocument : Count = 0
For i = LBound(Placeholders) To UBound(Placeholders) Parts = Split(Placeholders(i), "=", 2) If UBound(Parts) >= 1 Then Key = "{" & Trim(Parts(0)) & "}" : Value = Parts(1) With Doc.Content.Find .Text = Key : .Replacement.Text = Value .Forward = True : .Wrap = 1 : .Execute(Replace:=2) End With Count = Count + 1 End If Next i ReplacePlaceholders = CountEnd Function
' Export the active document to PDFFunction ExportToPDF(PDFPath) On Error Resume Next Application.ActiveDocument.ExportAsFixedFormat _ OutputFileName:=PDFPath, ExportFormat:=17, OpenAfterExport:=False ExportToPDF = (Err.Number = 0)End Function
' Insert text with specific formattingSub InsertFormattedText(Text, Style) With Application.Selection Select Case Style Case "Bold": .Font.Bold = True Case "Italic": .Font.Italic = True Case Else: .Font.Bold = False: .Font.Italic = False End Select .TypeText Text:=Text End WithEnd SubBuild the protected DLL that will replace your source code.
Click “Publish Final DLL” in the ribbon.
Click “Build Final DLL Files”.
VBA Padlock produces three DLLs in a bin subfolder next to your document:
DocumentBuilderrun32.dll (32-bit runtime)DocumentBuilderrun64.dll (64-bit runtime)DocumentBuilder.dll (Your compiled code)The VBA Bridge is the connection between your Word document and the DLL.
Open your Word file in Microsoft Word.
In VBA Padlock, click Create VBA Bridge → Inject Into Office.
VBA Padlock adds the VBADLLBridge module to your Word project.
Now you can call your compiled functions from regular Word VBA code using VBAPL_Execute.
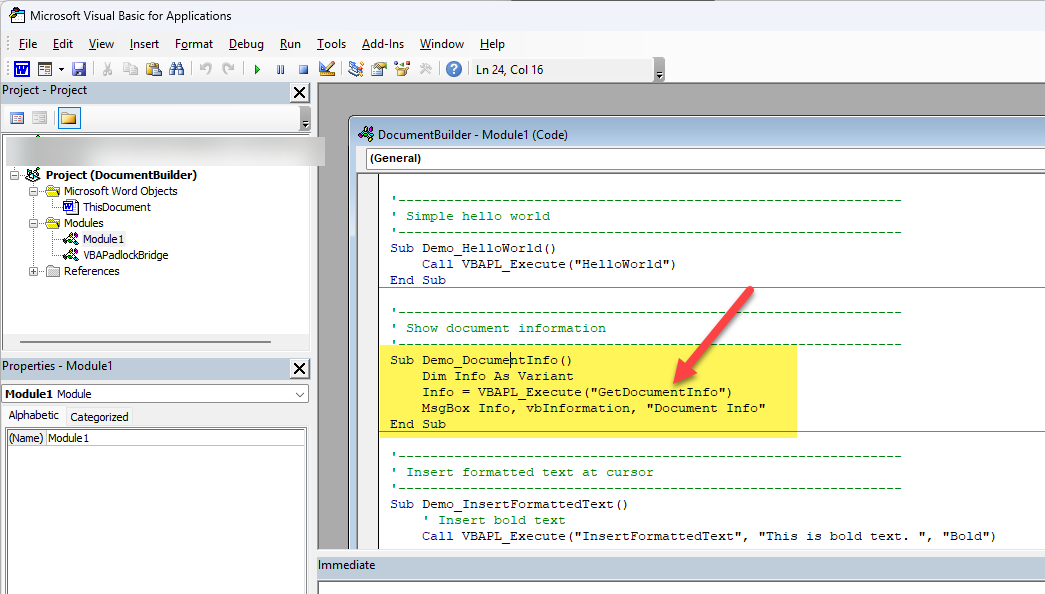
In the Word VBA Editor (Alt+F11), create a new module and add this:
'---------------------------------------------------------------' Simple hello world'---------------------------------------------------------------Sub Demo_HelloWorld() Call VBAPL_Execute("HelloWorld")End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------' Show document information'---------------------------------------------------------------Sub Demo_DocumentInfo() Dim Info As Variant ' Call the compiled DLL function Info = VBAPL_Execute("GetDocumentInfo") MsgBox Info, vbInformation, "Document Info"End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------' Insert formatted text at cursor'---------------------------------------------------------------Sub Demo_InsertFormattedText() ' Insert bold text Call VBAPL_Execute("InsertFormattedText", "This is bold text. ", "Bold")
' Insert italic text Call VBAPL_Execute("InsertFormattedText", "This is italic text. ", "Italic")
' Insert normal text Call VBAPL_Execute("InsertFormattedText", "This is normal text.", "Normal")End Sub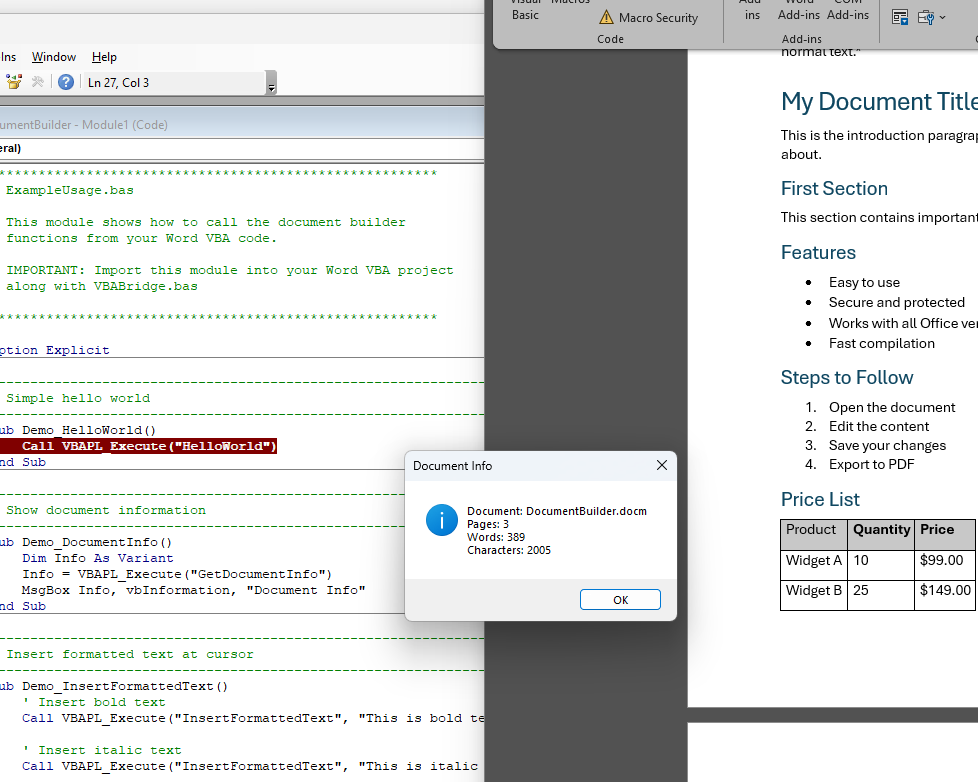
To require an activation key before your document can be used:
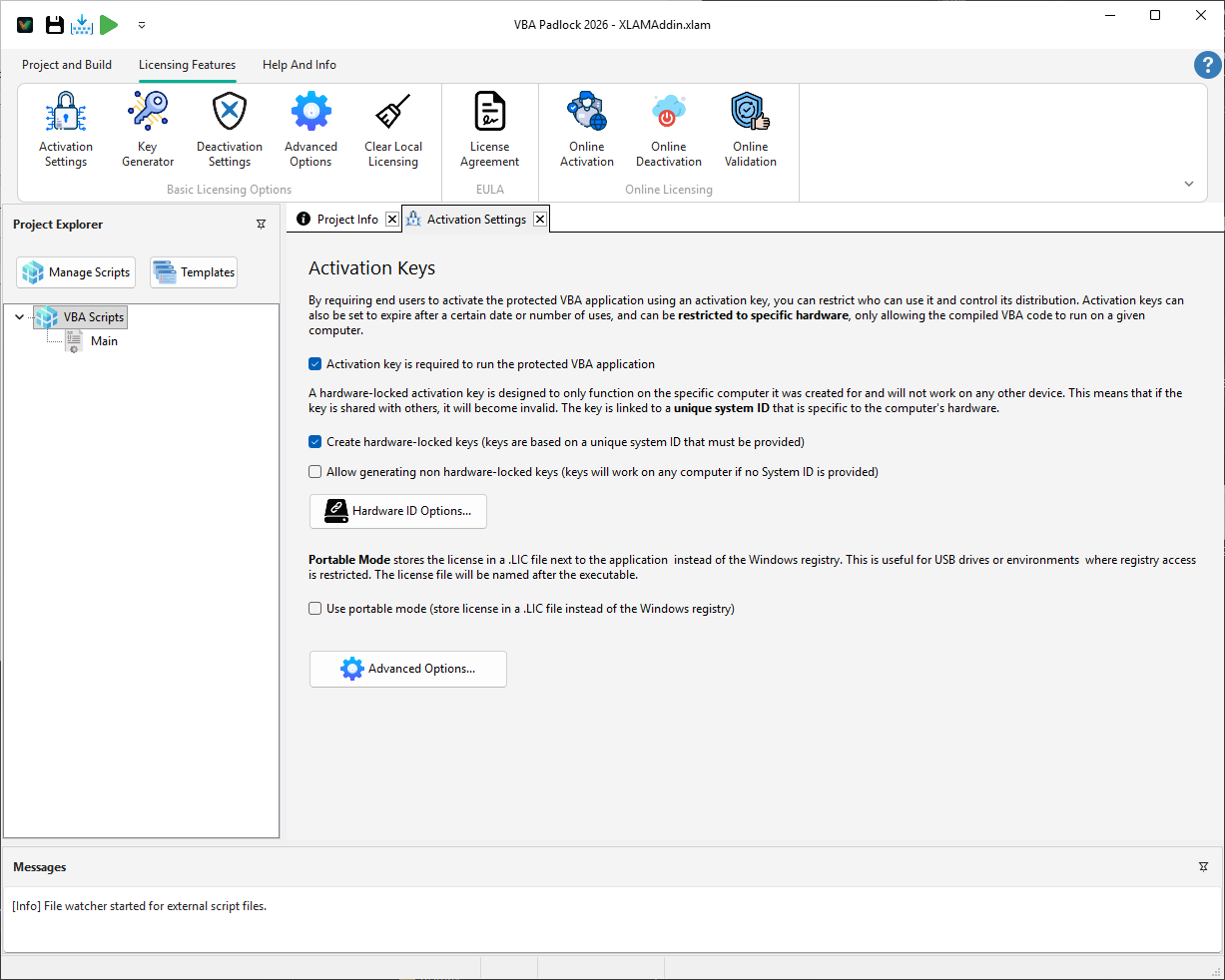
Go to Licensing Features → Activation Settings.
Check Activation key is required.
Optional: Enable Hardware Locking to tie licenses to specific PCs.
Rebuild the DLL to apply the security settings.
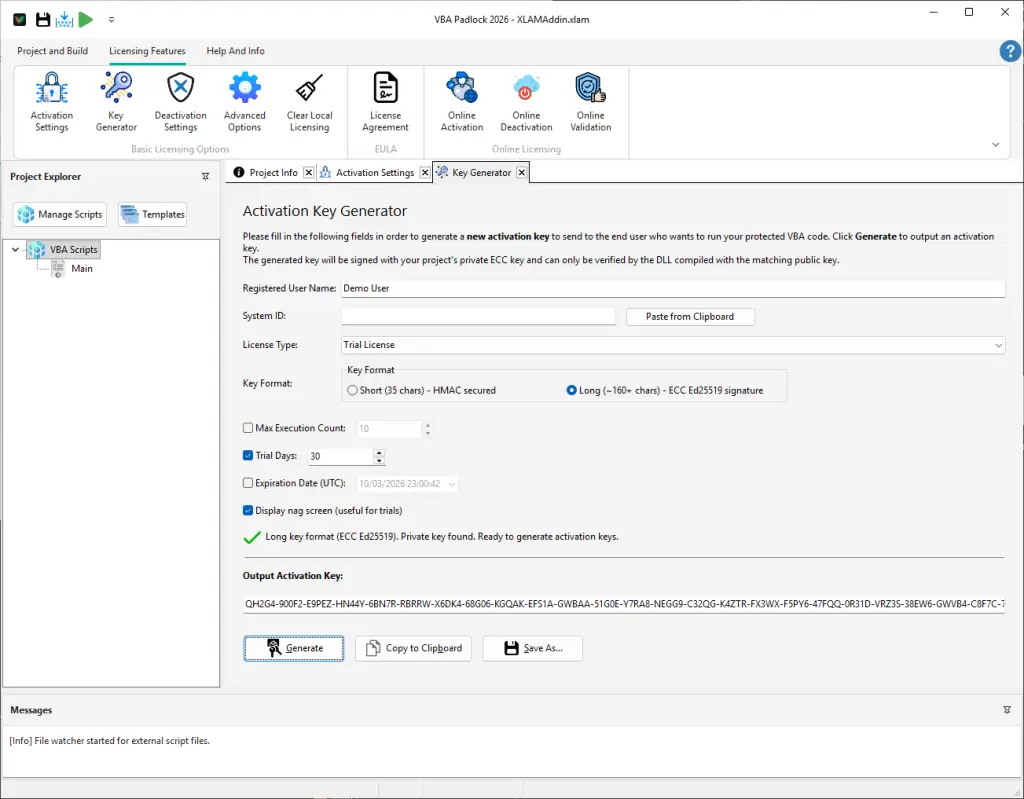
Generate a test key in the Key Generator.
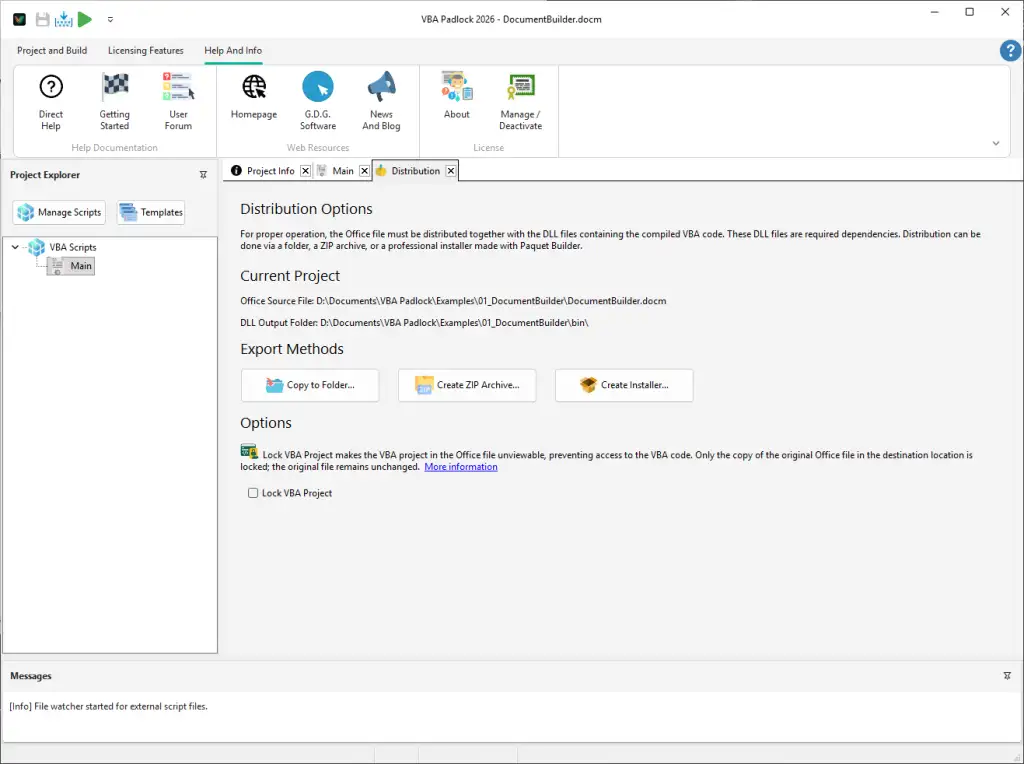
Package your application for release.
Click Distribute in the ribbon.
Select Create ZIP Archive.
The archive will contain your .docm file and the bin folder (mandatory).
Protect Excel
Similar workflow tailored for Excel workbooks. Read the guide →
Online Activation
Automate license activation over the internet. Read the guide →
VBA Bridge API
Full reference for all VBAPL_* functions.
View API reference →
VBA Compatibility
Check supported VBA features and statements. View reference →