Excel Constants
~2,900 xl* and rgb* constants for full Excel automation.
VBA Padlock ships with a set of ready-to-use script libraries — .bas modules containing thousands of Office VBA constants and utility functions that you can add to any project. These libraries let you use named constants like xlCenter, wdAlignParagraphLeft, or msoShapeRectangle directly in your compiled scripts, without needing a type library reference.
Excel Constants
~2,900 xl* and rgb* constants for full Excel automation.
Word Constants
~2,200 wd* constants for document formatting and manipulation.
PowerPoint Constants
~1,000 pp* constants for slides, transitions, and effects.
Access Constants
~1,400 ac* constants for forms, reports, and data operations.
Office Shared
~3,350 mso* constants for shapes, fills, and shared UI elements.
Utility Libraries
Error handling and Financial functions ready for your business logic.
Learn how to import these modules into your VBA Padlock project in three easy steps.
Open the Templates gallery
In the VBA Padlock code editor, click the Templates button in the toolbar.
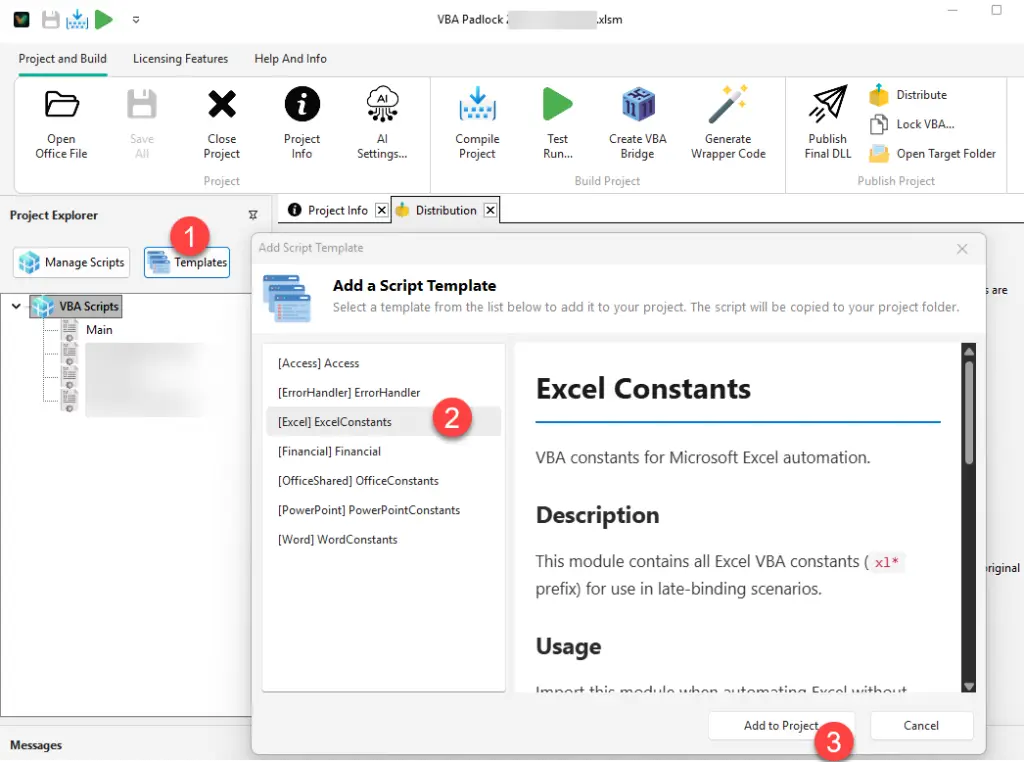
Select the library you need
Browse the categorized list on the left and click any library to preview its content and documentation.
Add it to your project
Click Add to Project. This creates a new .bas module in your project containing all the constants or functions from the selected library.
Once a library module is part of your project, any other module can access its constants by adding a References directive at the very top of the file.
For instance:
References ExcelConstants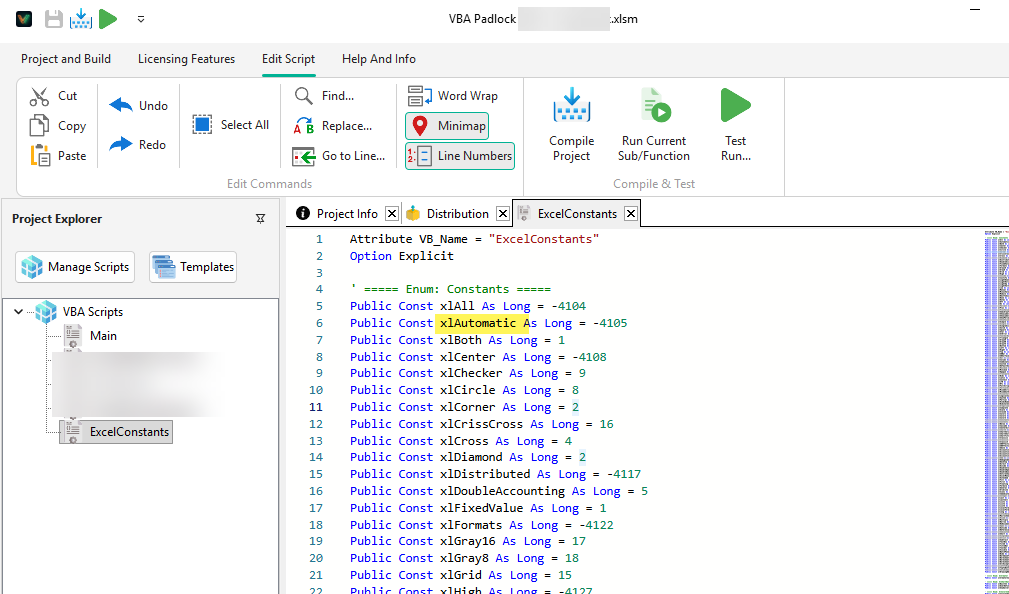
References directive must appear before any Option statement or code.References lines.Explore the constants available for each Microsoft Office application.
Contains ~2,900 constants for automating Microsoft Excel. Covers the most commonly used xl* enumerations plus 150+ named RGB colors.
Key Categories:
| Category | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment | xlCenter, xlLeft, xlRight | 20+ |
| Borders | xlContinuous, xlDash, xlDot | 15+ |
| Charts | xlColumnClustered, xlLine, xlPie | 40+ |
| Colors | rgbRed, rgbBlue, rgbCornflowerBlue | 150+ |
| Formats | xlOpenXMLWorkbook, xlCSV, xlAddIn | 40+ |
Example:
References ExcelConstants
Function FormatReport() Dim WS Set WS = Application.ActiveSheet WS.Range("A1:D1").HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter WS.Range("A1:D10").Borders.LineStyle = xlContinuous WS.Range("A1:D1").Interior.Color = rgbSteelBlue FormatReport = "Done"End FunctionContains ~2,200 constants for automating Microsoft Word. Covers paragraph formatting, document units, find/replace, and more.

Key Categories:
| Category | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment | wdAlignParagraphLeft, wdAlignParagraphCenter | 9 |
| Units | wdCharacter, wdWord, wdParagraph | 16 |
| Breaks | wdPageBreak, wdSectionBreakNextPage | 11 |
| Formats | wdFormatDocument, wdFormatPDF, wdFormatRTF | 24+ |
| Tables | wdTableFormatSimple1, wdTableFormatElegant | 42+ |
Example:
References WordConstants
Function FormatDocument() Dim Doc Set Doc = Application.ActiveDocument Doc.Paragraphs(1).Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenter Doc.Range.InsertBreak wdPageBreak Doc.Tables(1).Borders.OutsideLineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle FormatDocument = "Done"End FunctionContains ~1,000 constants for automating Microsoft PowerPoint. Covers slide layouts, transitions, animation effects, and export formats.
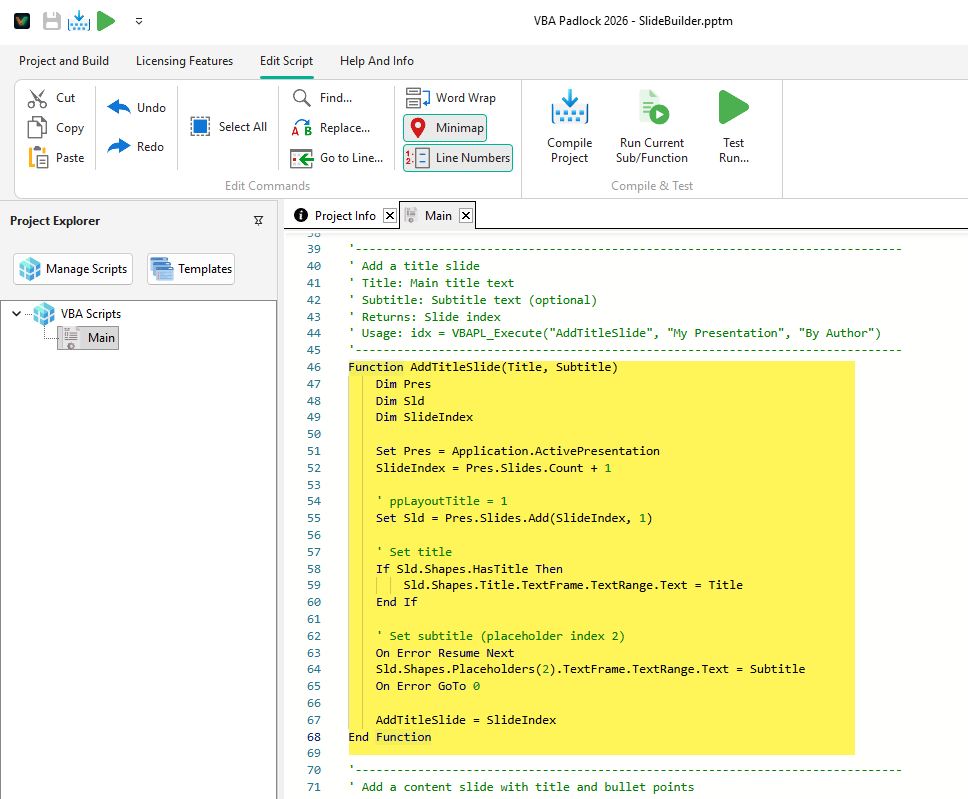
Key Categories:
| Category | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Layouts | ppLayoutTitle, ppLayoutText, ppLayoutBlank | 36 |
| Effects | ppEffectFade, ppEffectPush, ppEffectWipe | 150+ |
| Animations | msoAnimEffectAppear, msoAnimEffectFly | 150+ |
| Formats | ppSaveAsPresentation, ppSaveAsPDF, ppSaveAsPNG | 40+ |
Example:
References PowerPointConstants
Function BuildSlides() Dim Pres Set Pres = Application.ActivePresentation Dim Slide1 Set Slide1 = Pres.Slides.Add(1, ppLayoutTitle) Slide1.SlideShowTransition.EntryEffect = ppEffectFade BuildSlides = Pres.Slides.CountEnd FunctionContains ~1,400 constants for automating Microsoft Access. Covers form/report operations, control types, and data transfer.
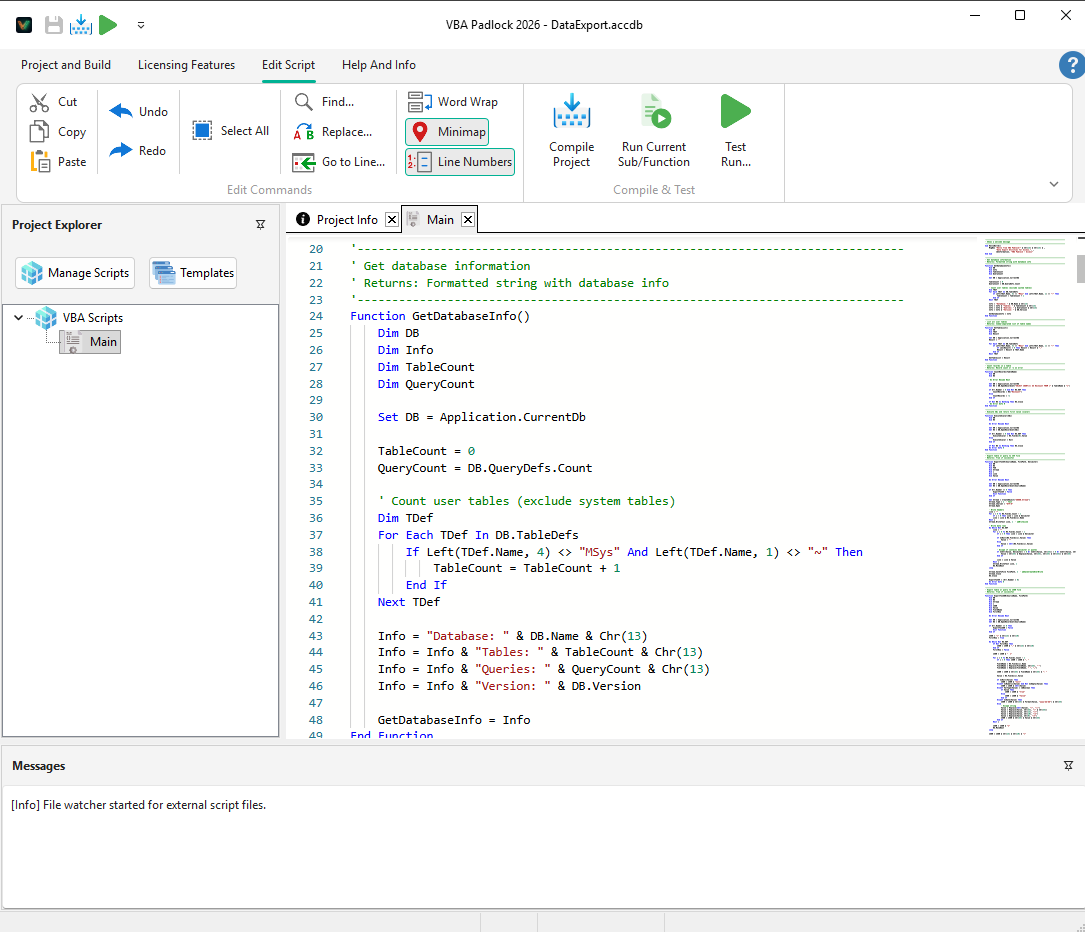
Key Categories:
| Category | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Objects | acForm, acReport, acQuery, acTable | 12 |
| Controls | acTextBox, acComboBox, acCommandButton | 29 |
| Transfer | acImport, acExport, acLink | 3 |
| Commands | acCmdRunMacro, acCmdSave, acCmdPrint | 50+ |
Example:
References AccessConstants
Function ExportTableData() Application.DoCmd.OpenForm "Customers", acNormal, , , acFormReadOnly Application.DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acExport, , "Orders", "C:\Output\Orders.xlsx" ExportTableData = "Exported"End FunctionContains ~3,350 shared MSO (Microsoft Office) constants used across all Office applications. These cover shapes, line styles, fill types, gradients, and more.
Key Categories:
| Category | Examples | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Shapes | msoShapeRectangle, msoShapeOval, msoShapeArrow | 183 |
| Fills | msoFillSolid, msoFillGradient, msoFillPattern | 6 |
| Gradients | msoGradientHorizontal, msoGradientVertical | 7 |
| Textures | msoTexturePapyrus, msoTextureMarble | 25 |
| 3D | msoMaterialMatte, msoMaterialMetal | 35+ |
Example:
References OfficeConstantsReferences ExcelConstants
Function AddShapes() Dim WS Set WS = Application.ActiveSheet Dim Shp Set Shp = WS.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 50, 50, 200, 100) Shp.Fill.OneColorGradient msoGradientHorizontal, 1, 0.5 Shp.Line.DashStyle = msoLineSolid AddShapes = "Shape added"End FunctionHelper modules for common programming tasks.
Provides 6 helper functions for structured error handling inside compiled scripts.
| Function | Signature | Description |
|---|---|---|
GetErrorInfo | GetErrorInfo() | Returns formatted string with Error details |
FormatError | FormatError(Num, [Desc]) | Returns formatted error message |
HasError | HasError() | True if Err.Number <> 0 |
ClearError | ClearError() | Clears the Err object |
Example:
References ErrorHandler
Function SafeDivide(A, B) On Error Resume Next SafeDivide = A / B If HasError() Then SafeDivide = "Error: " & GetErrorInfo() ClearError End IfEnd FunctionProvides 12 financial calculation functions covering loans, investments, and asset depreciation.
Calculations Included:
PMT, PV, FV, NPer, Rate, IPMT, PPMTNPV, IRRSLN, SYD, DDBExample — Loan payment:
References Financial
Function CalculateMortgage(LoanAmount, AnnualRate, Years) Dim MonthlyRate, Months MonthlyRate = AnnualRate / 12 Months = Years * 12 CalculateMortgage = Abs(PMT(MonthlyRate, Months, LoanAmount))End FunctionScript Functions
Built-in functions for License, Locale, and more.
VBA Compatibility
Supported VBA features and limitations.
Code Editor
Learn how to use the VBA Padlock code editor.
VBA Bridge
Call compiled functions from your Office VBA code.