VBA to DLL — How VBA Compilation Works
VBA Padlock compiles your VBA macros into native 32-bit and 64-bit Windows DLLs. The original source code is replaced by bytecode that cannot be decompiled.
What Is VBA to DLL Compilation?
VBA to DLL compilation is the process of transforming your VBA source code into native Windows DLL files containing compiled bytecode. Unlike obfuscation (which scrambles readable code) or password protection (which hides it behind a removable flag), compilation produces a completely different binary format — the original VBA simply does not exist anymore.
VBA Padlock handles the entire pipeline: parsing, bytecode generation, DLL packaging, code signing, and VBA Bridge generation. You write standard VBA code in a dedicated IDE, click Publish, and receive ready-to-distribute signed DLLs.
The Compilation Pipeline
Four steps from VBA source code to signed, distributable DLL files.
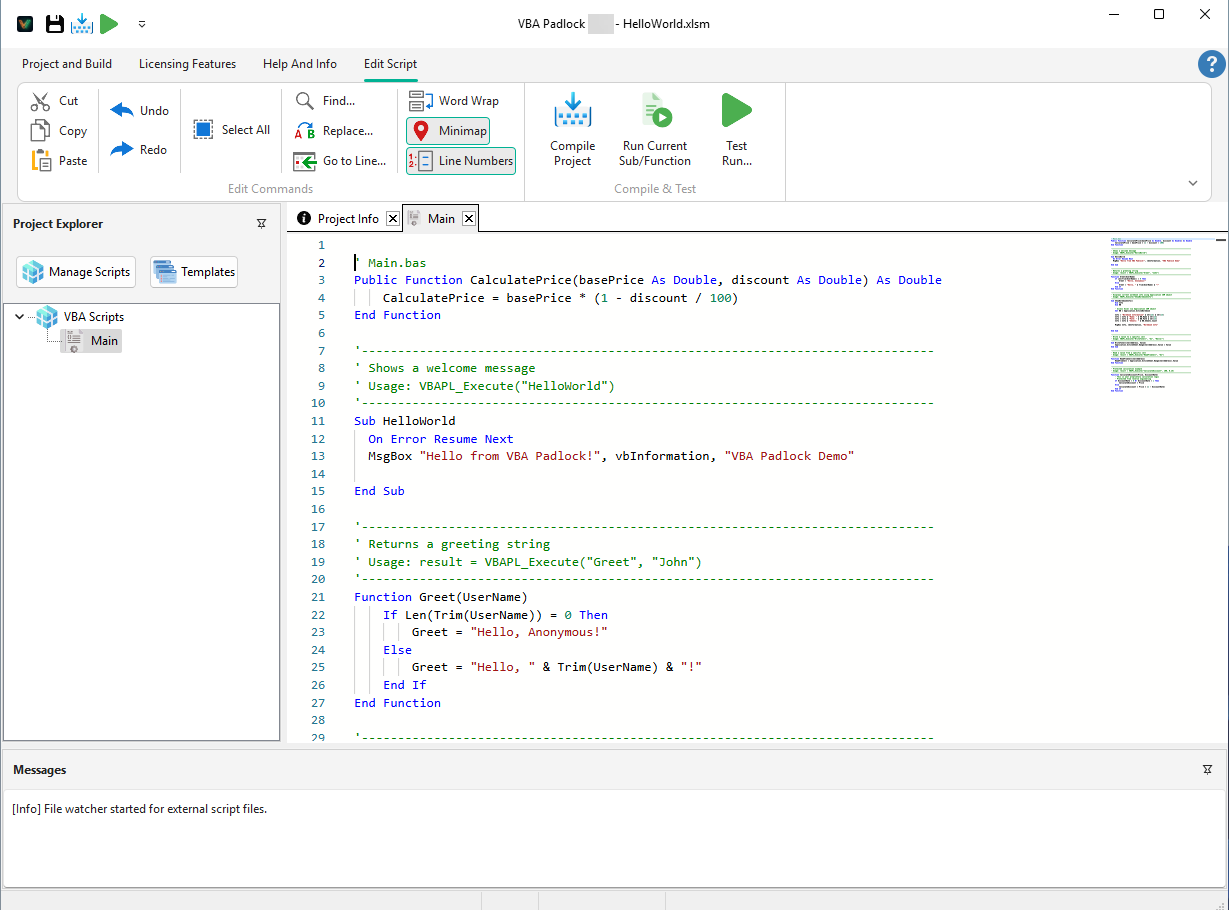
Write VBA Code
Write your macros in VBA Padlock Studio — a dedicated IDE with syntax highlighting, autocomplete, and module management.
Compile to Bytecode
Click Compile. VBA Padlock parses your VBA, resolves references, and transforms each function into bytecode stored in a satellite DLL.
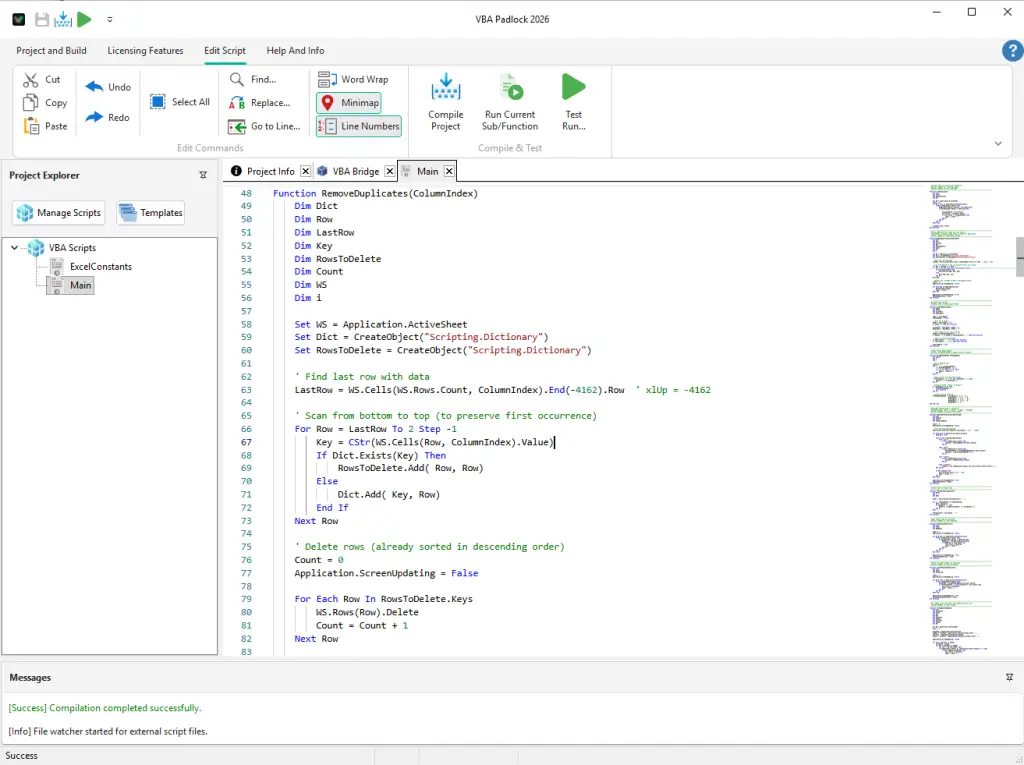
Publish Signed DLLs
Click Publish. VBA Padlock produces signed 32-bit and 64-bit runtime DLLs plus the satellite DLL containing your compiled code.
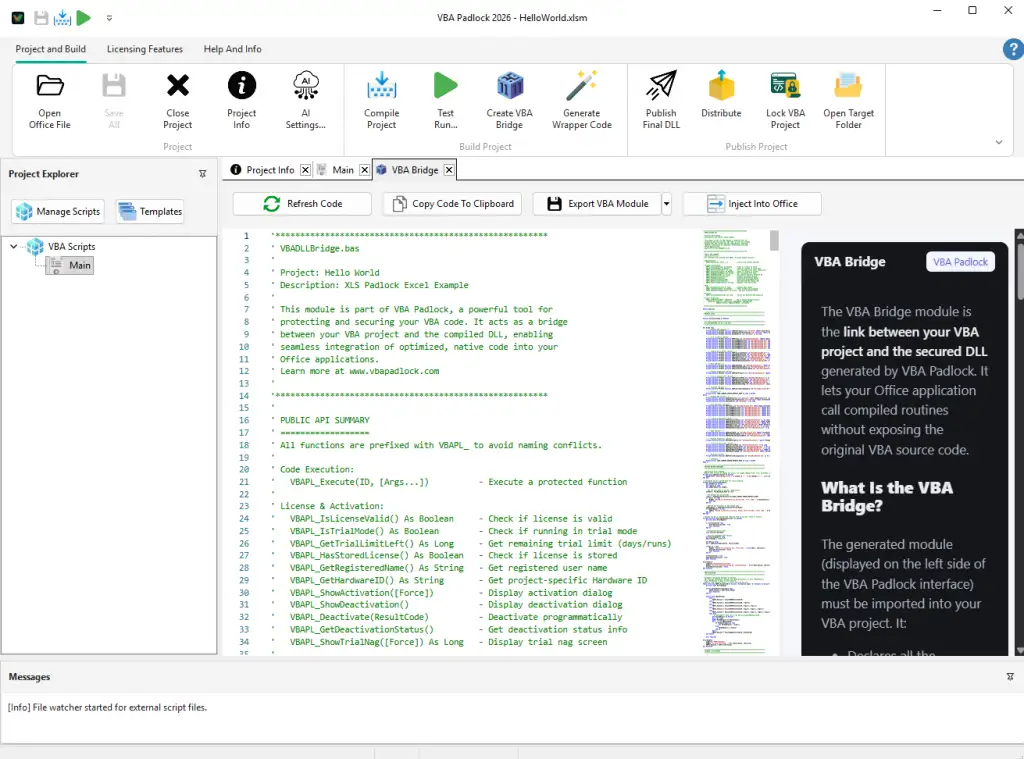
Generate VBA Bridge
A thin VBA module is generated automatically. It loads the DLL and routes calls from your Office file to the compiled functions.
The Compilation Process in VBA Padlock
From the code editor to compiled DLL output — see the process in action.
What VBA Padlock Produces
After compilation, your project folder contains the protected Office file and a
bin/
directory with three DLL files. This is the complete distribution package — nothing else is needed.
MyProject/
├── MyProject.xlsm ← Office file (VBA Bridge only)
└── bin/ ← DLL directory
├── MyProjectrun32.dll ← 32-bit runtime (Authenticode-signed)
├── MyProjectrun64.dll ← 64-bit runtime (Authenticode-signed)
└── MyProject.dll ← Satellite DLL (compiled bytecode)| File | Purpose | Signed |
|---|---|---|
| {Name}run32.dll | Runtime for 32-bit Office | |
| {Name}run64.dll | Runtime for 64-bit Office | |
| {Name}.dll | Satellite DLL with compiled bytecode | Optional |
Before and After Compilation
Left: the VBA code you write in VBA Padlock Studio. Right: what users see in the VBA Editor — only the Bridge module.
Function ProcessData(InputRange, OutputCell)
Dim Total As Double
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To InputRange.Rows.Count
Total = Total + InputRange.Cells(i, 1)
Next i
Application.ActiveSheet _
.Range(OutputCell).Value = Total
ProcessData = Total
End Function' VBA Bridge — auto-generated by VBA Padlock
' This module loads the compiled DLL and
' routes function calls. No business logic.
Sub RunProcessData()
Dim Result As Variant
Result = VBAPL_Execute( _
"ProcessData", _
Range("A1:A100"), "B1")
MsgBox "Total: " & Result
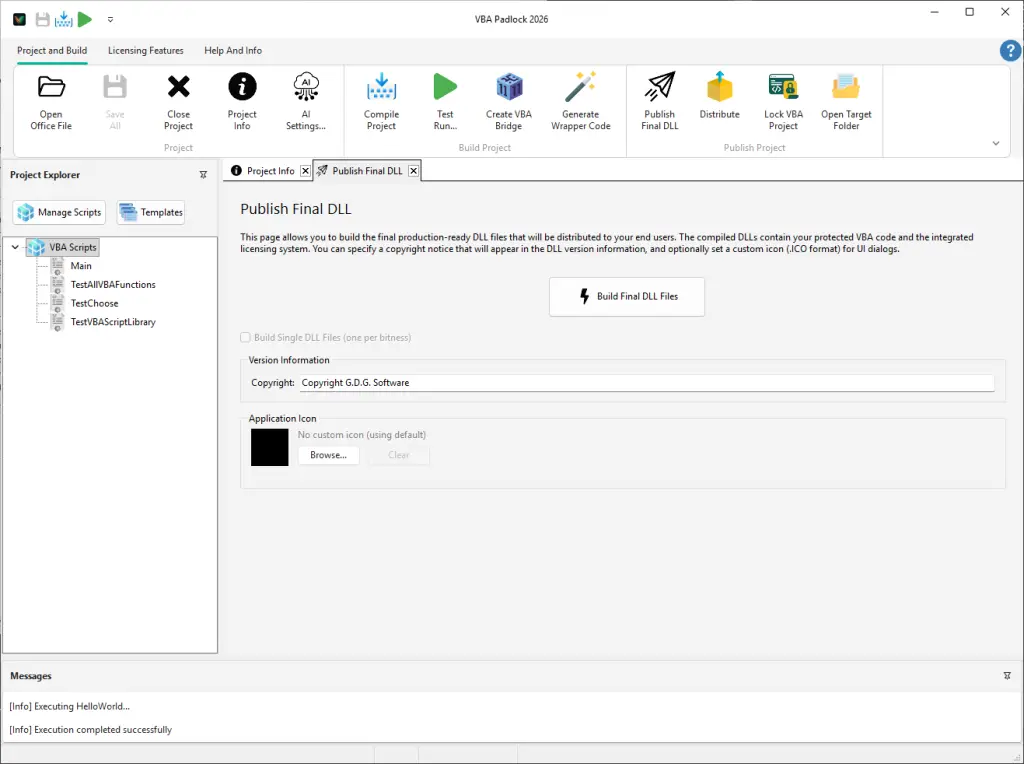
End SubPublish and Distribute
Publish signed DLLs and generate the VBA Bridge module with a single click.
What DLL Compilation Gives You
Compilation is not just about protection — it's a complete distribution framework for professional VBA applications.
Source Code Removed
Your VBA source is compiled into bytecode. There is no readable code left in the Office file or in the DLL. The VBA Editor shows only the Bridge module.
COM Access Preserved
All COM object calls (Application, Workbooks, Documents, Ranges, Recordsets) work exactly as before. The bytecode interpreter handles COM interop seamlessly.
Digitally Signed Output
Runtime DLLs are Authenticode-signed by G.D.G. Software. Windows SmartScreen, antivirus software, and corporate policies trust the signed binaries.
Dual Architecture
Every project produces both 32-bit and 64-bit DLLs. The VBA Bridge loads the correct runtime automatically based on the user's Office installation.
Built-in Licensing
Add license keys, hardware locking, trial periods, and online activation — all compiled into the DLL. No extra code needed in your Office file.
Zero Dependencies
End users need only Microsoft Office (2016+). No runtime, no .NET Framework, no admin rights. Ship your Office file with the bin/ folder and you're done.
Learn More
Deep dive into the compilation engine
Why VBA passwords don't protect code
Why obfuscation is not enough
Monetize with licensing and distribution
Why you need a VBA compiler and how it works
Ready to Secure Your VBA Code?
Download VBA Padlock and start compiling, protecting, and licensing your VBA macros today.