Protect Your Word VBA Code from Reverse Engineering
Compile Word macros into native DLLs — your document automation, templates, and mail merge logic stay hidden inside compiled bytecode.
Why VBA Password Protection Fails for Word
If you distribute Word documents or templates with VBA macros, your code is at risk. The built-in VBA project password can be removed in seconds using freely available tools. Once bypassed, anyone can read, copy, or modify your macros — including document generation logic, mail merge algorithms, and proprietary formatting routines.
Third-party "obfuscators" only rename variables and add junk code. The logic remains in plain VBA, fully readable in the Visual Basic Editor. For commercial Word add-ins and templates, this offers no real protection.
The Solution: Compile Word VBA to Native DLLs
VBA Padlock takes a fundamentally different approach. Instead of hiding VBA source code behind a breakable password, it compiles your macros into native 32-bit and 64-bit DLLs. The original VBA code is transformed into bytecode that cannot be decompiled back to the source.
Your Word document (.docm) or template (.dotm) contains only a thin VBA Bridge module — a few lines of code that load the DLL and route function calls. All your intellectual property lives inside the compiled DLL, completely invisible to anyone opening the VBA Editor.
Write
Write your Word VBA macros in VBA Padlock Studio with syntax highlighting and autocomplete.
Compile
Click Publish to compile into signed 32-bit and 64-bit DLLs. A VBA Bridge is generated automatically.
Distribute
Ship your .docm or .dotm with the bin/ folder. Users run macros normally — the DLL handles everything.
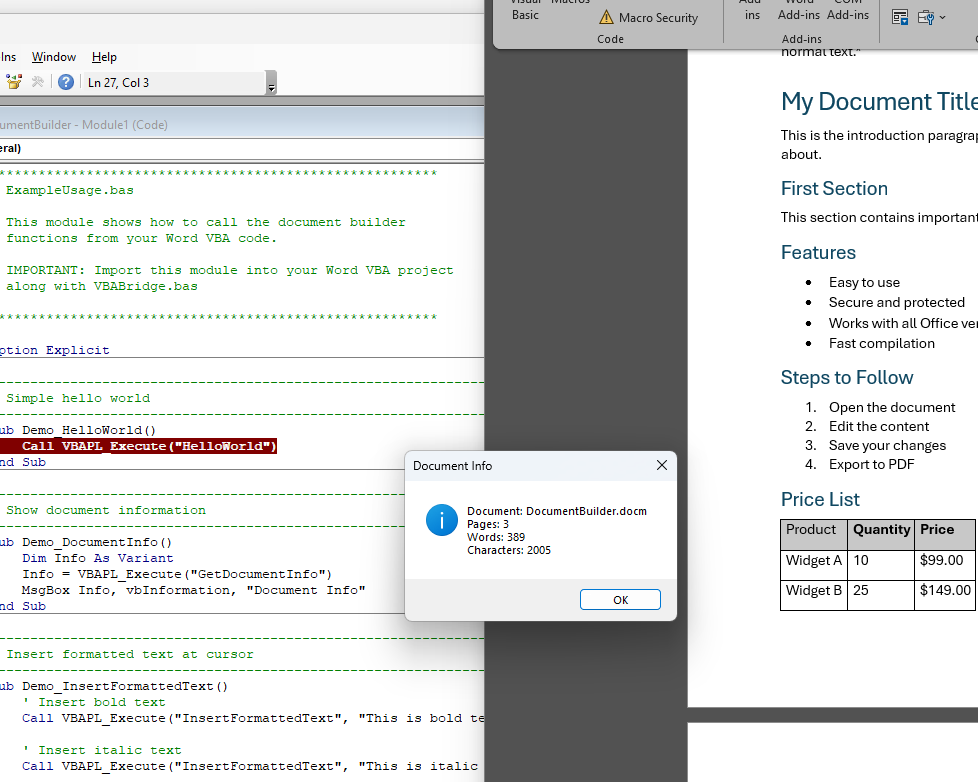
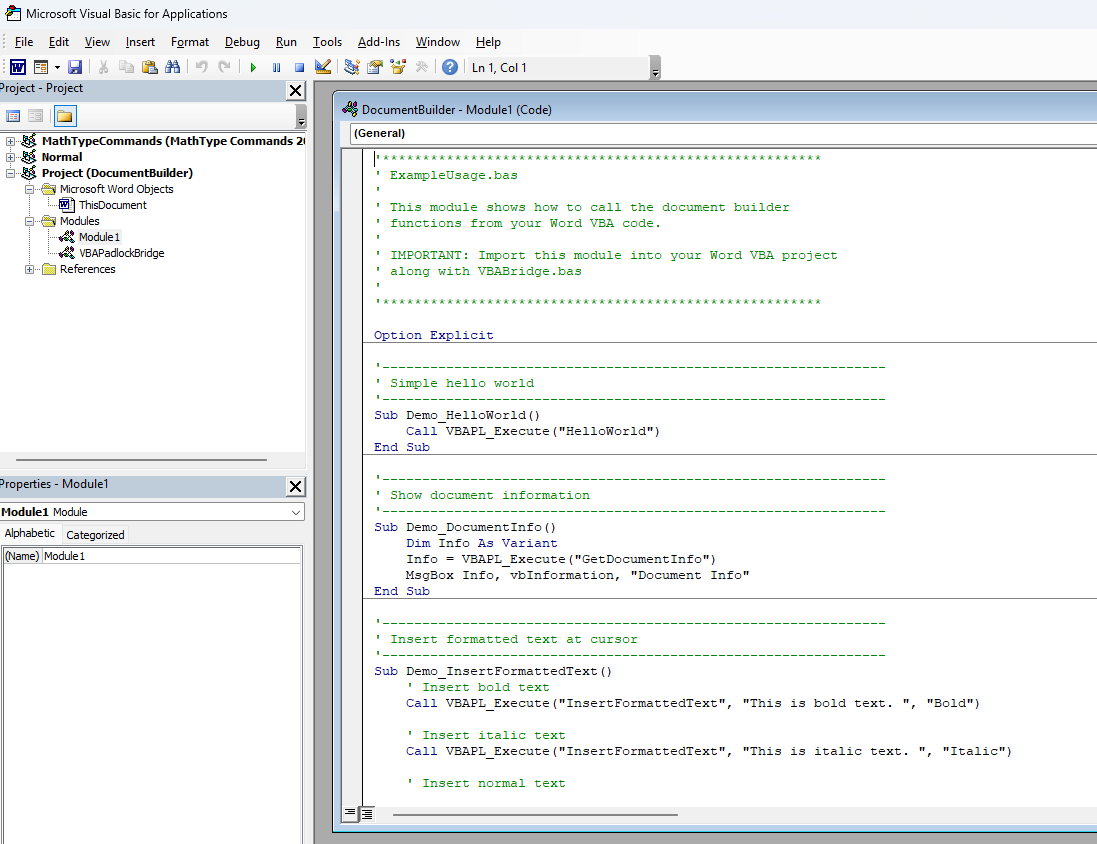
See It in Action
Left: your protected code compiled into the DLL. Right: the thin VBA caller in your Word document.
Function ReplacePlaceholders(Placeholders)
Dim Doc, i, Parts, Key, Value
Set Doc = Application.ActiveDocument
For i = LBound(Placeholders) To UBound(Placeholders)
Parts = Split(Placeholders(i), "=", 2)
Key = "{" & Trim(Parts(0)) & "}"
With Doc.Content.Find
.Text = Key
.Replacement.Text = Parts(1)
.Execute Replace:=2
End With
Next i
End FunctionSub FillTemplate()
Dim Data As Variant
Data = Array( _
"CLIENT=Acme Corp", _
"DATE=" & Format(Date, "MMMM d, yyyy"), _
"AMOUNT=$15,000")
Call VBAPL_Execute("ReplacePlaceholders", Data)
MsgBox "Template filled!", vbInformation
End SubWord VBA Protection in Action
Real template and document automation examples protected with VBA Padlock.
What You Can Protect in Word
VBA Padlock supports all Word VBA scenarios — from simple document macros to commercial template engines and .dotm add-ins.
Template & Add-in Protection
Compile .dotm templates and Word add-ins into secure DLLs. Distribute your automation tools without exposing a single line of source code.
Document Generation
Protect contract builders, proposal generators, and automated report engines that create complex Word documents from data sources.
Mail Merge Automation
Secure proprietary mail merge logic — data source connections, field mapping, conditional formatting — inside compiled bytecode.
Find & Replace Engines
Hide advanced search-and-replace, placeholder substitution, and content transformation algorithms from prying eyes.
PDF Export Tools
Ship document-to-PDF conversion tools with protected formatting, watermarking, and layout logic.
Licensing & Activation
Add hardware-locked license keys, trial periods, and online activation to any Word VBA project — built into the DLL.
Need a step-by-step walkthrough?
Read the dedicated Word tutorial
Follow the full process to protect a Word document or template with VBA Padlock.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can VBA Padlock compile Word templates (.dotm) and add-ins?
Does my compiled code still have access to the Word object model?
How do I protect a mail merge automation built with Word VBA?
Will end users need to install anything besides Microsoft Word?
Can I add license key activation to my Word VBA project?
Ready to Secure Your VBA Code?
Download VBA Padlock and start compiling, protecting, and licensing your VBA macros today.
Related Pages
Protect Excel workbooks, add-ins, and UDFs
Protect Access database logic and queries
Protect presentation macros and add-ins
How the compilation pipeline works
Why you need a VBA compiler and how it works